11 Essential Things You Must Know About Container Homes
Container buildings are gaining increasing attention for their flexibility, fast construction, and eco-friendliness. This article provides an in-depth analysis of container construction, covering interior and exterior treatments, construction timelines, sound and heat insulation, foundation requirements, and main advantages. It also explores the primary applications of container buildings.
Construction Timeline for Container Buildings
The construction of a container building typically takes 2 to 4 weeks, depending on project size, design complexity, and infrastructure preparation. With prefabricated container modules, only foundational work, assembly, and finishing are required on-site, significantly reducing construction time.
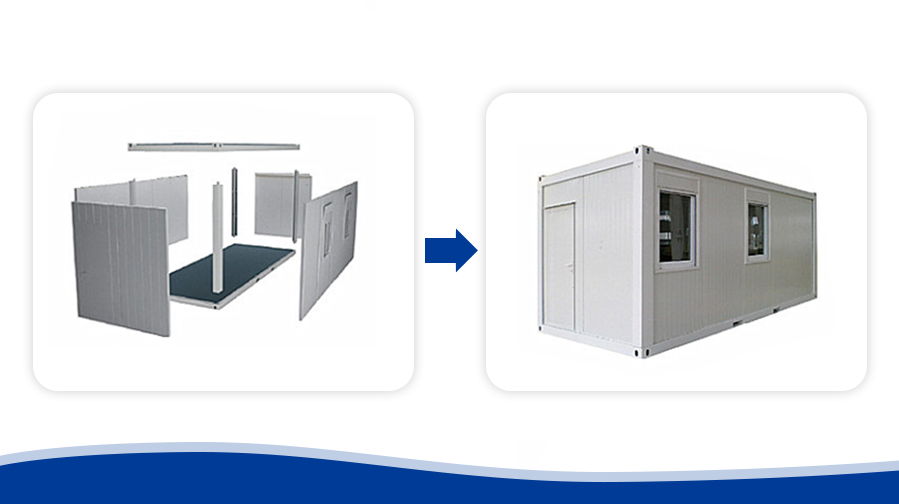

Lifespan of Container Buildings
Container buildings generally have a lifespan of 15 to 30 years, determined by material quality, environmental conditions, and regular maintenance. High-quality materials and regular upkeep can substantially extend the building’s lifespan.
Interior and Exterior Wall and Roof Finishing
Interior finishes often use materials like light steel frames and gypsum board to improve insulation and soundproofing. Walls can be covered with wallpaper, paint, or decorative panels, and insulation layers can be added to improve comfort for residential use.
For exterior walls, corrosion and waterproofing treatments are necessary based on environmental conditions, typically using fluorocarbon or anti-corrosion paint. Aluminum composite panels can also be added for enhanced durability and aesthetics in demanding environments.
The roof can be equipped with waterproof layers or thermal insulation materials to prevent overheating in summer.
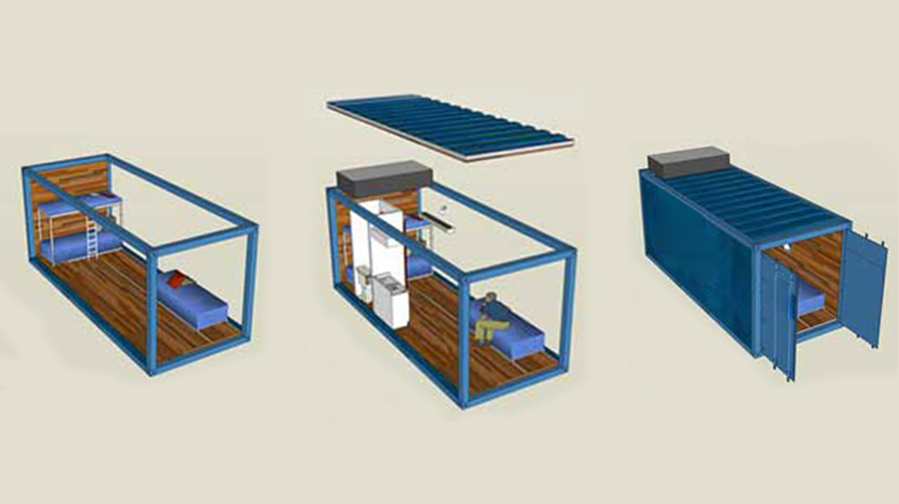
Waterproofing Techniques
Waterproofing mainly targets the roof and joining areas:
-Roof: Generally waterproofed with membrane layers, polyurethane coatings, or additional waterproof panels to minimize rainwater penetration.
-Walls: Exterior walls are treated with waterproof or anti-corrosion paint, and seams are sealed to prevent rust from rain exposure.
-Seams: Rubber seals or waterproof adhesives are used in between container joins to prevent leaks.
Insulation Techniques
For insulation, external materials like polyurethane boards or thermal coatings can mitigate heat from direct sunlight. Internally, light steel frames with gypsum boards filled with insulation materials enhance thermal protection.
Soundproofing Techniques
Containers provide basic soundproofing; however, for high residential comfort, soundproof materials like acoustic wool or soundproof panels can be added to walls to reduce noise.

Foundation Requirements
Container buildings typically require a simple foundation that ensures a level surface with adequate load-bearing capacity. For heavier structures, the foundation should be more robust with proper drainage to prevent sinking or tilting. Common foundation types include concrete slabs, steel structures, and screw pile foundations.
Advantages of Container Buildings Over Traditional Structures
-Quick Construction: Prefabricated modules reduce on-site construction time.
-Mobility: Container buildings can be relocated, ideal for rapid deployment.
-Low Cost: Overall costs are low, making them suitable for temporary or budget-friendly projects.
-Eco-Friendly: Containers are recyclable, aligning with environmental sustainability goals.
-High Strength: The material is corrosion-resistant and earthquake-proof, suitable for various geographic conditions.
Advantages of Huji Products
- Use of high-quality anti-corrosion materials to extend product lifespan.
- Modular and flexible designs tailored to meet diverse requirements.
- Efficient manufacturing processes ensure timely delivery.
- Comprehensive support from design to after-sales service to guarantee successful project execution.

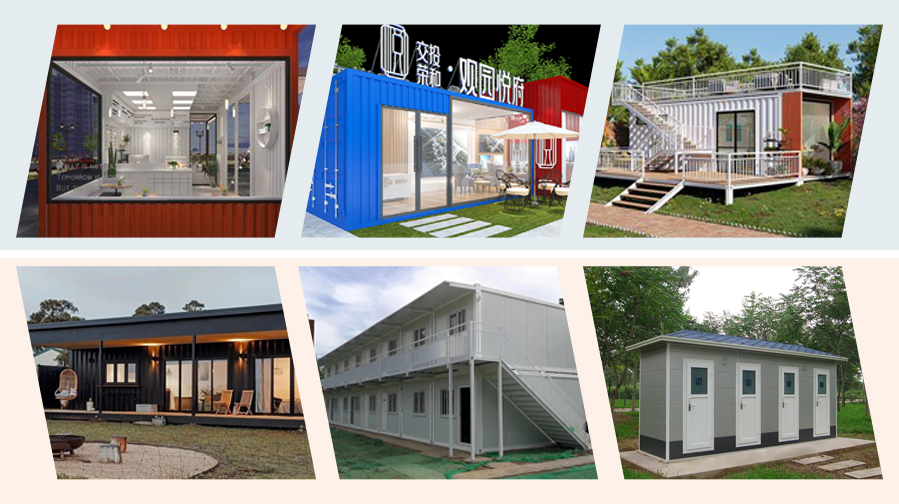
Applications of Container Buildings
- Temporary commercial projects, such as cafes, shops, and pop-up stores.
- Exhibitions and showrooms for easy setup and takedown.
- Mobile hotels or unique lodgings in scenic areas to attract tourists.
- Temporary or permanent housing for budget-conscious residential needs.
- Quick setup for shelters and service facilities post-disaster.
- Public amenities, like restrooms or waiting rooms, offering flexibility and convenience for urban infrastructure.

Installation Considerations for Container Homes
When installing container buildings, keep in mind the following:
-Foundation Preparation: Ensure the foundation is flat and stable to prevent tilting. Drainage should be included to minimize corrosion.
-Joining and Securing: For multi-container structures, ensure sealed joints to avoid water and air leakage.
-Utility Layout: Plan the layout of electrical and water lines during installation to avoid rework.
-Wind and Earthquake Resistance: Ensure the container structure meets local wind and earthquake standards, especially in high-wind or earthquake-prone areas. Reinforce key joints as necessary.

 Viktor Remel
Viktor Remel