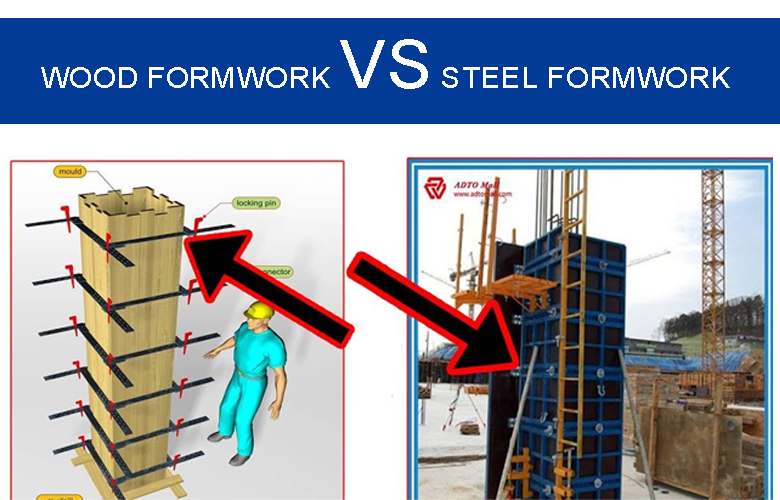
Material and Manufacturing Process of Steel Formwork
Selected Materials - Q235B and Q345B Steel
Steel formwork is primarily made from Q235B and Q345B steel, both of which offer excellent strength and toughness. Q235B is a carbon structural steel, while Q345B is a low-alloy, high-strength structural steel, making them suitable for high-load construction. They provide durable, stable support for building structures.

High-Precision Manufacturing Process
The production process of steel formwork ensures stable performance and durability, including the following key steps:
- Welding Process: High-precision welding techniques are used to ensure the structural stability and durability of the formwork, meeting high-load construction requirements.
- Surface Treatment: Corrosion-resistant treatments or coating techniques are applied to extend the formwork's lifespan, keeping it in good condition even in harsh environments.
Key Advantages of Steel Formwork
High Strength and Excellent Compressive Performance
Steel formwork boasts outstanding compressive and bending resistance, making it ideal for high-load and large-span construction projects. Its superior strength outperforms traditional wooden and plastic formwork, providing reliable support for large-scale projects.
Strong Durability and Multiple Reuses
Steel formwork is highly durable, resistant to wear and corrosion, and can withstand multiple cycles of use, significantly reducing project costs. Its long lifespan and stability ensure its durability in various construction conditions.
High Construction Efficiency and Convenient Assembly/Disassembly
Steel formwork is designed with a modular system, making installation and disassembly quick and easy. The simple assembly process enhances construction speed and reduces project timelines, especially for time-sensitive projects.
Smooth Surface, Meeting High-Standard Construction Requirements
The finely processed surface of steel formwork is smooth and flat, requiring no additional treatment after construction. This greatly enhances the aesthetics and quality of the building surface.
Common Specifications and Technical Parameters of Steel Formwork
| Parameter | Description |
| Material | Q235B/Q345B |
| Thickness | Customizable: 3mm, 4mm, 6mm, etc. |
| Surface Treatment | Anti-rust coating, galvanization, oil coating, etc. |
| Load Capacity | Suitable for large-span, high-load construction needs |
| Applications | High-rise buildings, bridges, tunnels, underground projects, etc. |
Diverse Applications of Steel Formwork
High-Rise Buildings and Residential Construction
In high-rise buildings, steel formwork is used for structural elements like load-bearing walls and floors, providing solid support. Its high strength meets modern safety standards, making it ideal for large-span buildings.
Bridge and Tunnel Projects
Steel formwork is widely used in bridge and tunnel construction, particularly for supporting structures such as piers and tunnel walls. Its high strength and corrosion resistance ensure outstanding stability even in complex construction environments.
Industrial Buildings and Storage Facilities
Steel formwork is used in industrial buildings like factories, warehouses, and hangars, where high structural strength is required. It provides strong and reliable support, significantly enhancing construction efficiency.
Underground Engineering and Hydraulic Facilities
Steel formwork is suitable for damp, complex underground projects and hydraulic facilities, effectively resisting corrosion and providing excellent support in the construction of dams, canals, and other water-related infrastructure.

Steel Formwork Application Case Studies
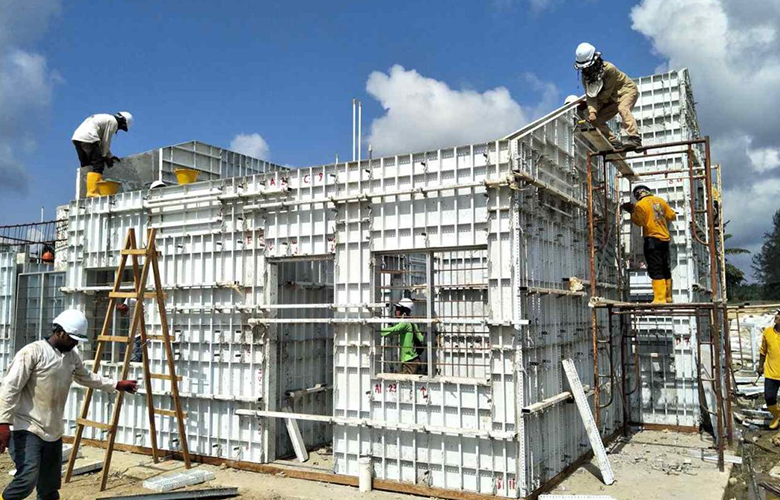
- Case Study 1: Steel formwork used for load-bearing walls in high-rise building construction, showcasing its exceptional load-bearing performance.
- Case Study 2: Steel formwork supporting bridge structures, demonstrating its stability and durability in bridge construction.
- Case Study 3: Application of steel formwork in industrial building wall construction, highlighting its efficient use in industrial facility projects.


 Viktor Remel
Viktor Remel